Arriving and Opening Reflections
Walking into the RCN PSI Alumni Conference at Cowdray Hall on that crisp November morning, I felt a mix of pride, gratitude, and curiosity. It’s been many years since I first began speaking at RCN events like this, yet every time feels new because each gathering brings together nurses, carers, service users, and leaders who continue to shape the future of mental health care.

Before I continue to describe the event, let me sum up the Royal College of Nursing PSI programme. Basically the Psychosocial Interventions (PSI) programme is a nationally recognised training initiative designed to strengthen therapeutic skills of mental health professionals and embed recovery-focused, relationship-based care across services.
The PSI program is rooted in the principles of collaboration, reflection, co-production and empowerment, PSI equips practitioners with practical tools to support individuals experiencing mental distress, while also valuing the insight of carers and families.
I think what makes PSI stand out is its emphasis on seeing people beyond their diagnosis and fostering empathy, curiosity, and shared understanding between nurses, service users, and carers.
At the start of the conference and during it, I spoke to a few nurses over coffee, each reflecting on how PSI had shaped their practice one mental health nurse told me it had helped her “find her voice again.” For me, as a carer with lived experience, it was great to witness this sense of renewal. It reminded me why collaboration between professionals and lived experience communities is so essential.
Around 10 a.m., Catherine Gamble formally opened the event, setting a tone of gratitude and shared learning. Her introduction reminded us how much the alumni network had grown and how lived experience was now firmly part of the PSI culture.

As someone with lived experience of caring for my mum, who lived with schizophrenia, I approached the events not just as an observer but as someone deeply invested in the stories and struggles that bring us together as a triangle.
When I was invited to open the event and share my reflections as a carer, I knew I wanted to do more than talk about carers, I wanted to speak for them, and with them.
My Opening Talk – “The Nurses Who Walk With Us”
Standing at the podium, looking out at rows of passionate mental health nurses and lived experience, I began with gratitude. My words were simple but heartfelt:
“This is really about the nurses who walk with us, the ones who move beyond the labels, beyond the charts, and see the person, not the problem.”

I read a poem I had written to honour the compassion and resilience of those in the room a piece I called The Nurses Who Walk With Us.

The poem spoke about presence, about listening, and about the small acts of care that ripple into great change.
After my talk, I was moved by the warmth of the response. Many came up to share how my words mirrored their experiences or reminded them of why they came into nursing. That moment of connection that shared understanding set the tone for the day.
The Locksmiths Animation and Alumni Showcase
Following our opening session, Ellie Gordon and Stephen Jones launched the new animation “We Are the Locksmiths.” The film poetically portrayed mental health nurses as key-cutters shaping, adapting, and helping people find the right fit for recovery.
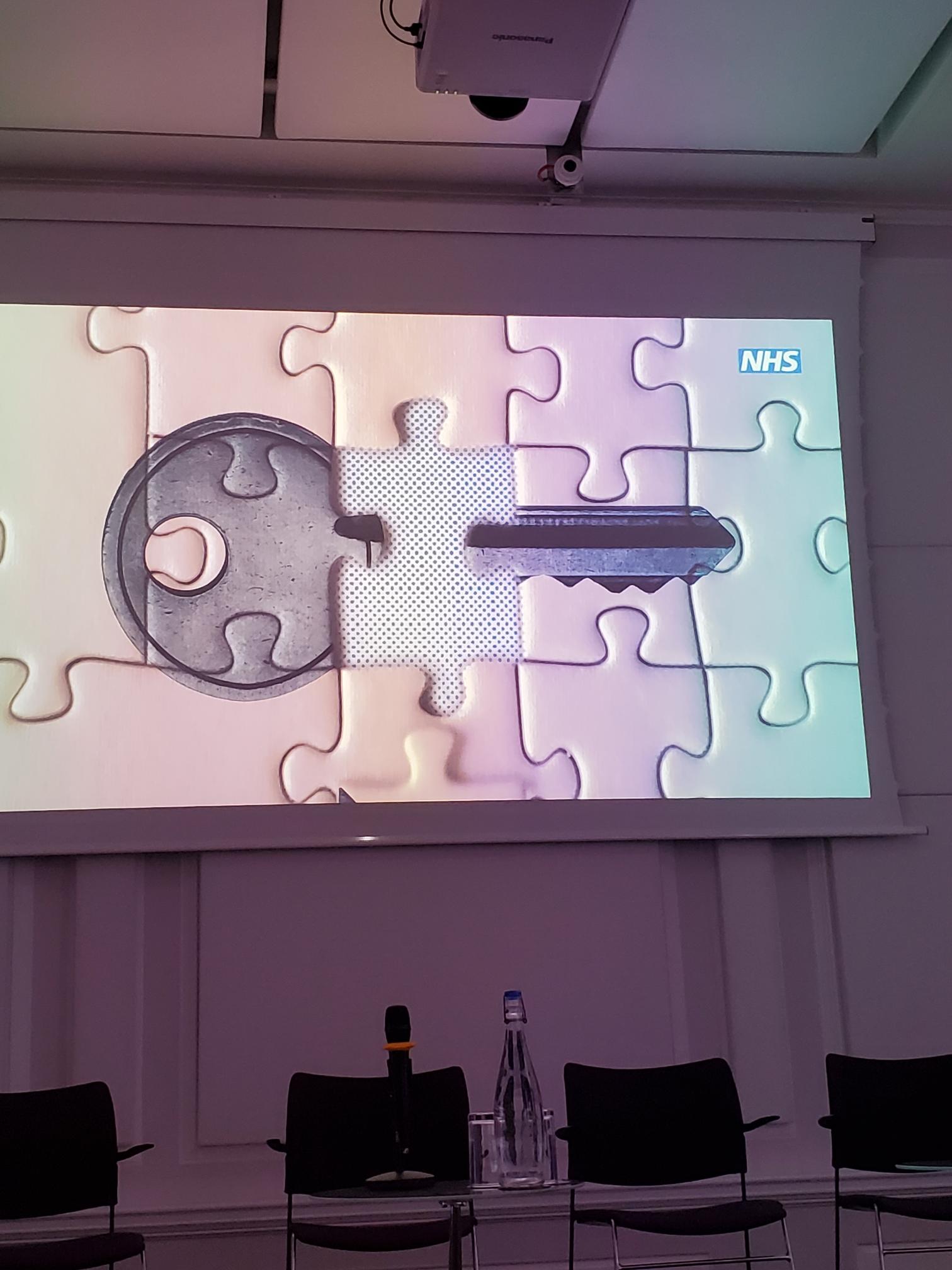

Watching it, I was struck by how accurately it captured the emotional labour of care, the balancing of vulnerability, patience, and professionalism
Next we had the Mentimeter session that morning, which was led by Professor Sally Hardy. She guided participants through reflective wellbeing questions using the interactive Mentimeter tool, encouraging everyone to think about how to sustain personal and professional wellbeing in mental health practice. Sally’s session wasn’t just about gathering feedback

Afterwards, the Alumni and Facilitators’ “Show and Tell Time” began. Groups from Sheffield NHS Trust, Sussex Mental Health Partnership, Lancashire Mental Health NHS trust, and Hereford NHS Trust sharing creative projects and reflections from their PSI practice. There were posters, poems, and community initiatives that had grown directly from the training. I wandered around the tables, speaking with participants who described how PSI had changed their teams. I think One mental health nurse told me, “We stopped seeing interventions as techniques and started seeing them as relationships.” It was inspiring
Workshop One – Working Together in Risk and Safety
After refreshments, we broke into workshops. I joined Workshop One: Lived Experience and Co-Production – Utilising Our Expertise, led by Hannah Cadogan and colleagues. It was energising to see lived experienced and mental health nurses working side by side.

I spoke about what co-production really means from a carer’s point of view. I shared my journey as someone who has cared for a family member living with schizophrenia and another with autism, and how those experiences taught me the importance of being included as an equal partner in care.

I explained that carers often hold a deep understanding of the person they support insights that can make a real difference if professionals take the time to listen and involve us from the start, not as an afterthought. Drawing on my work with Carers UK, the Carers Trust, and the Triangle of Care as many nurses from the mental health trusts were members of triangle of care programme., I spoke about how true co-production is built on trust, openness, and shared learning.
We discussed barriers time, fear, power differences but also solutions, like embedding co-production in supervision and reflective practice.
In this session, the discussion turned to how we can meaningfully involve carers and service users in planning safety not as tick-box exercises, but as genuine collaborations. I found myself reflecting on my own experiences of sitting in meetings where decisions were made about my mum rather than with us.
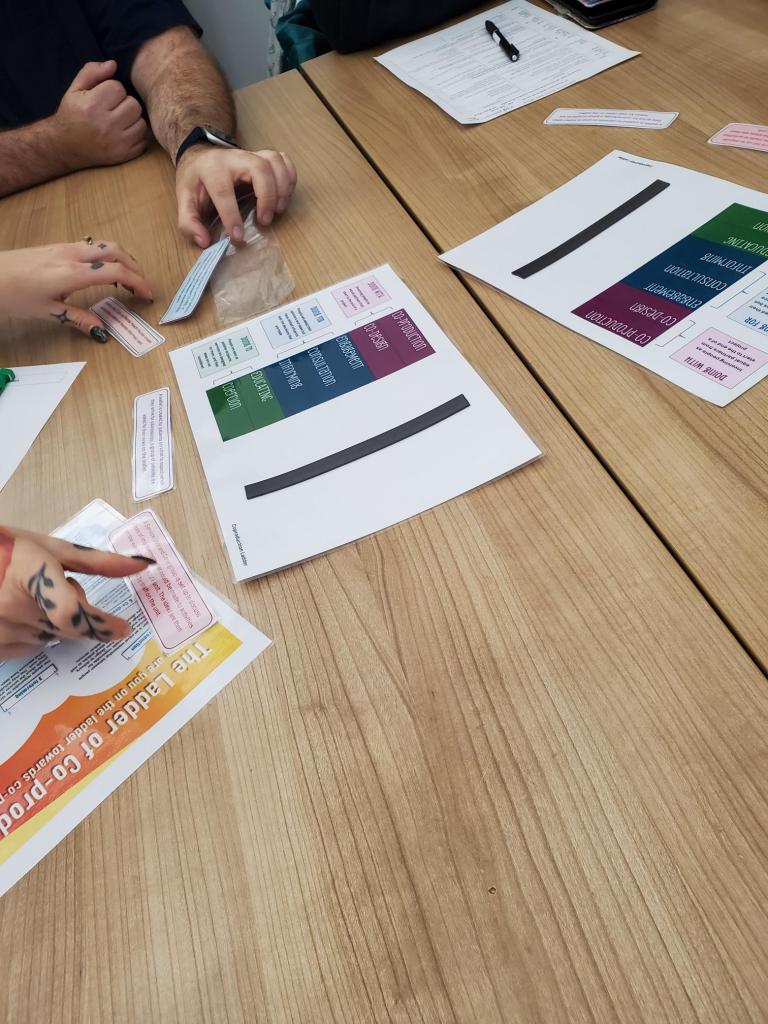

Hearing the nurses speak so openly about their challenges about time pressures, fear of getting it wrong, and the emotional toll of risk reminded me that we’re all human in this process. True co-production means sharing not only responsibility but also vulnerability.

One participant spoke about the importance of patience: “We’re not here to fix; we’re here to find a way in.” That line stayed with me. It echoed my own philosophy that care starts with listening, not solving.
By the end of the workshop, we agreed that co-produced safety isn’t about removing risk; it’s about building trust so we can face risk together.
Workshop Two – Co-Production and Carer Involvement
Lunch provided another opportunity for networking. The Mental Health Forum stand and MHP stall displayed resources on psychosocial practice.




I met others who had recently completed the course.

Conversations were open, curious, and full of mutual respect the kind of professional empathy that sustains hope in challenging work.
After lunch we heard from Professor Nicola Ranger, RCN General Secretary, who welcomed everyone back, commending the alumni for sustaining PSI’s legacy. Her words “you are the custodians of compassion” perfectly captured the spirit of the day.

The evaluation session of the RCN PSI Alumni Conference was presented in partnership with London South Bank University (LSBU), who have been key academic collaborators in examining the outcomes and long-term impact of the Psychosocial Interventions (PSI) programme. This section was introduced by Stephen Jones, and Professor Chris Flood, a leading figure in mental health nursing and research at LSBU.

Together, they outlined how LSBU’s evaluation seeks to capture not just the quantitative outcomes of PSI such as improved confidence and competence among practitioners but also the qualitative stories of change, growth, and compassion that the alumni community embodies.
There will be several teams at LSBU, but I was impressed on the make up of the Advisory and Supervisory Team provides academic oversight and strategic direction.
- Professor Patrick Callaghan, Professor of Mental Health Science at LSBU, offers extensive expertise in psychosocial interventions and nursing research leadership.
- Professor Chris Flood, a leading mental health and adult nurse researcher, specialises in health economics, survey design, and qualitative inquiry.
- Professor Neil Brimblecombe, Professor of Mental Health and Learning Disability, contributes his expertise in workforce development, nurse prescribing, and policy analysis linking the PSI evaluation to broader NHS workforce strategies.
- Professor Eddie Chaplin, an expert in intellectual disabilities and psychosocial interventions, supports the development of inclusive frameworks for peer support, guided self-help, and service co-production.
Afternoon workshop
In the afternoon, I attended Workshop Three: Working Together in Risk – Co-Production, Suicide and Personalised Safety. It was deeply emotional. We discussed how carers can be crucial in early warning and safety planning, but only if professionals create safe spaces for them to speak. The workshop was presented by Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trus
During the workshop, we took part in reflective exercises that encouraged us to consider what “shared safety” truly means. We were asked to think of times when communication broke down between families, patients and professionals, and how different outcomes might have been possible if trust and collaboration had been stronger.
Celebrating Archievements
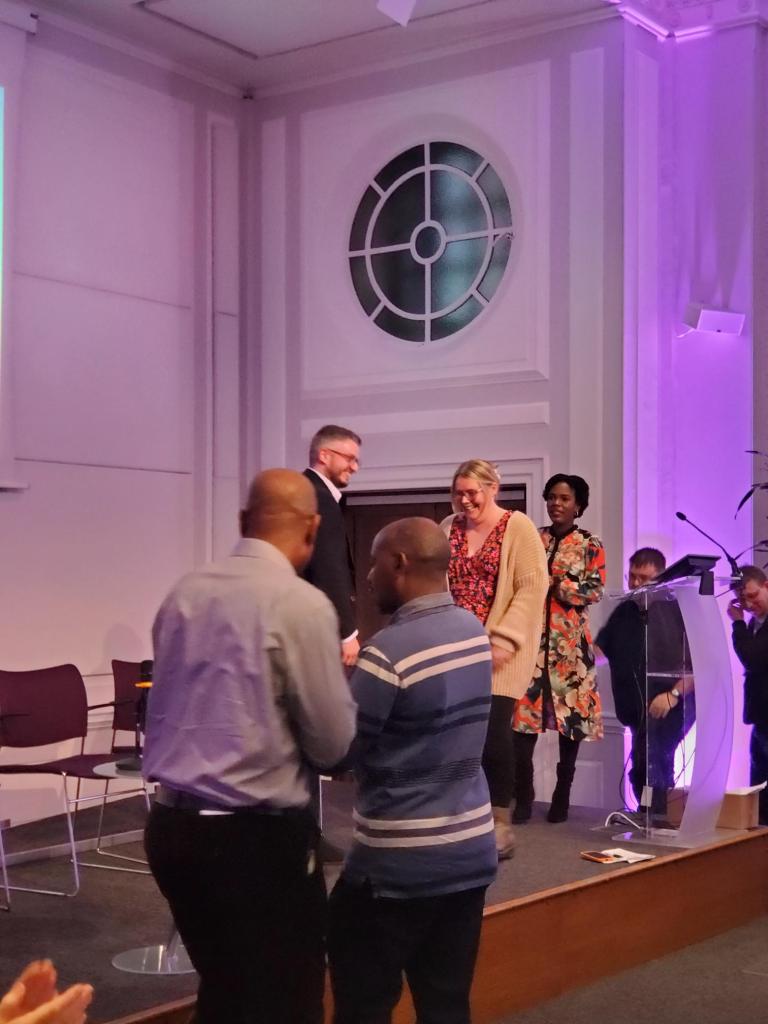



Those who finished the RCN PSI programm were presented with a RCN PSI alumni badge, which i felt was a small but powerful symbol of commitment, compassion, and continued learning. For many, receiving that badge wasn’t just about completing a programme; it represented belonging to a network that values empathy, partnership, and the courage to keep improving mental health care together.
Reflections and Looking Ahead
As the day drew to a close, we took a quiet moment to reflect. Conferences like this are not just about learning they are about belonging. They remind me that, while the caring role can often feel isolating, there is a wider network of understanding and solidarity.

I missed out a lot more that took place at the alumni event, but watch out for more exciting news from the RCN in future.
To find out more about the RCN PSI Progamme, click link below.