Overview of the Forum
The National Ethnic Mental Health Carer Forum is a grassroots group that focuses on addressing the unique challenges ethnic minority carers face in the mental health care system. The forum brings together carers, professionals, and organizations to engage in discussions, share experiences, and advocate for the inclusion of carers’ voices, especially those from minority backgrounds, in mental health policy and practice.
The forum acknowledges the significant role carers play in supporting individuals with mental health issues, especially from ethnic minority communities. It also highlights the issues of systemic and structural racism within the mental health care system and how these issues affect not only patients but also their carers.
I began the discussion by focusing on the importance of anti-racism in the mental health care system, especially as it pertains to ethnic minority carers. I explained that the forum’s main aim was to address the challenges faced by ethnic minority carers in mental health, emphasizing how systemic racism continues to affect these carers and their loved ones.
I highlighted the following key points:
- Racism as a Structural Issue:
- Racism in mental health care is not just about individual prejudice, but it is deeply embedded in the structure of the system. This includes policies and practices that disproportionately affect ethnic minority communities.
- I pointed out that ethnic minority carers face unique challenges in navigating the mental health care system, including being excluded from important discussions about their loved ones’ care. I stressed that carers those who know the patients best often feel their voices are undervalued or completely ignored by mental health professionals.
- Racial inequalities manifest in various ways, from higher rates of detention under the Mental Health Act to the overuse of restraint and coercive care practices. These practices disproportionately affect ethnic minority communities, and the role of carers is often marginalized in these processes.
- Importance of Carers’ Voices:
- I made it clear that carers’ voices must be heard when it comes to anti-racism efforts in mental health services. Carers have the ability to provide crucial context about their loved ones’ needs, especially cultural needs, that clinicians may overlook or misinterpret.
- It was crucial to stress that carers are not just supporters of the patient; they are knowledge holders with unique insights into the patient’s condition, behaviors, and needs. Without including them, mental health services risk misunderstanding cultural expressions of distress, leading to misdiagnosis or inappropriate treatment.
Requests for Future Presentations from Prof. Subodh Dave and Ruth:

- Greater Focus on Mental Health Policy Reforms:
- Attendees requested further discussions on the mental health policy reforms and the steps being taken to ensure that these changes address racial disparities. They expressed interest in hearing more about the impact of recent changes and how policy could be further improved to support ethnic minority communities.
- Practical Examples of Anti-Racism Initiatives:
- Participants asked for real-world examples of anti-racism initiatives being implemented within mental health services. They wanted to hear about successful case studies where changes have been made and how those changes have positively impacted carers and patients.
- Integration of Carers in Mental Health Decision-Making:
- There was a strong interest in exploring how carers can be better integrated into decision-making processes at a systemic level. Attendees wanted Prof. Dave and Ruth to discuss strategies to ensure that carers are not just involved in individual care but are included in the larger policy decisions that shape mental health services.
- Cultural Competency Training for Professionals:
- Attendees suggested that cultural competency training should be a central focus in future discussions. They wanted to understand how mental health professionals are being trained to understand the unique cultural contexts of ethnic minority communities and how this is being addressed through institutional change.
- Long-term Strategy for Addressing Racial Disparities:
- Attendees requested a long-term strategy for addressing racial disparities in mental health services. They were particularly interested in future initiatives, including how diversity in the workforce and access to care for ethnic minority communities would evolve over time.
Questions Asked During the Discussion:
- How can we ensure that mental health professionals take racial disparities seriously?
- What role can ethnic minority carers play in tackling systemic racism in mental health services?
- What are the next steps in ensuring that ethnic minority carers are involved in mental health policy at every level?
- Can you discuss the intersection of race and mental health legislation and how it specifically affects ethnic minority carers?
- How can cultural competency training be integrated into everyday practice for mental health professionals?
Presentation by Dr. Patrick Nyikavaranda: Policy, Equity & Carer Engagement
Next up to speak was Dr. Patrick Nyikavaranda is a Senior Research Fellow and the Public Involvement and Engagement Lead at the NIHR Mental Health Policy Research Unit within the Division of Psychiatry at University College London (UCL). His work focuses on improving mental health policy through research that aims to address equity and inclusion in mental health services.
Dr. Nyikavaranda has a strong commitment to engaging carers and patients with lived experience in the research process, ensuring that their voices are central to shaping mental health care policies and creating more equitable services. He is particularly focused on addressing the systemic racial disparities in mental health care and promoting cultural competence among mental health professionals.
Key Points from Dr. Nyikavaranda’s Presentation:
- Overview of the Policy Research Unit:
- Dr. Nyikavaranda explained the work of the Policy Research Unit in Mental Health, which is focused on generating evidence to influence mental health policy and improve mental health services.
- The unit works with a range of stakeholders, including carers, to produce evidence that informs the development of policy aimed at addressing racial disparities and improving care for ethnic minority communities in the mental health system.
- Carer Engagement:
- A central theme of Dr. Nyikavaranda’s presentation was the importance of involving carers in mental health research and policy. He emphasized that carers are essential partners in the mental health care process and their insights and lived experiences are crucial in shaping equitable services.
- Carers’ lived experiences offer unique perspectives on the challenges faced by patients, especially those from ethnic minority backgrounds, and their input is invaluable in creating policies that are more inclusive and culturally competent.
- Addressing Equity in Research and Policy:
- Dr. Nyikavaranda spoke about the persistent inequities in mental health services, particularly for ethnic minority patients. He discussed the importance of research that focuses on equity, specifically how racial disparities impact access to services, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes.
- He highlighted the need for inclusive research that represents the voices of carers, especially those from underrepresented communities. Engaging carers in the research process ensures that the evidence produced reflects the real-world needs of patients and carers.
After Dr. Nyikavaranda’s presentation, the session continued with a discussion and Q&A where forum participants had the opportunity to ask questions and provide reflections on the topic of policy, equity, and carer engagement in mental health.
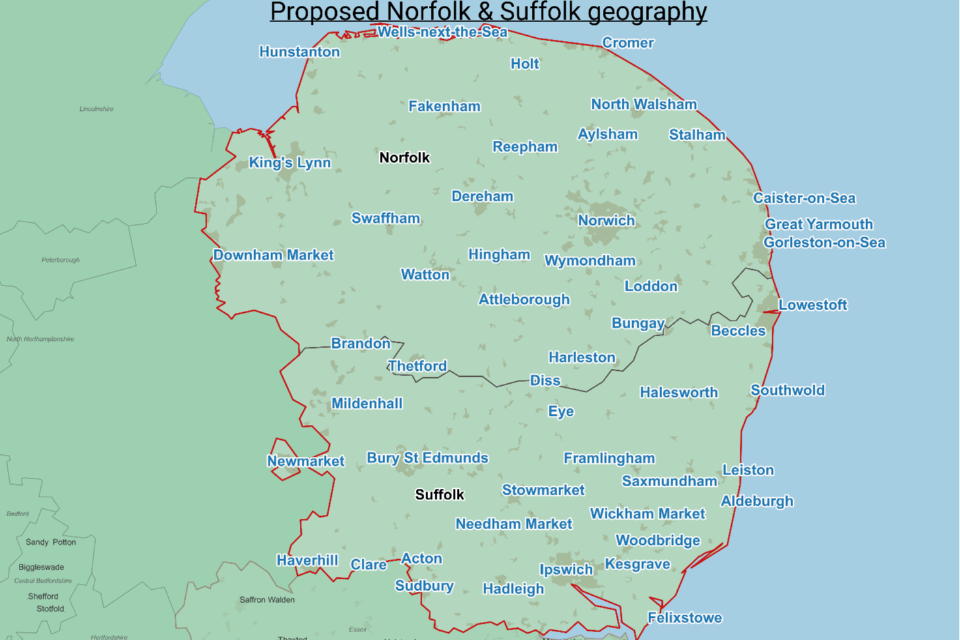
Updates from Norfolk and Suffolk Foundation Trust
During the forum representatives from Norfolk and Suffolk Foundation Trust (NSFT), provided updates on the progress made in involving carers, particularly those from ethnic minority backgrounds, in improving mental health services and addressing racial disparities.
The key updates from Norfolk and Suffolk Foundation Trust were as follows:
- Carer Engagement:
- Norfolk and Suffolk Foundation Trust has made significant strides in engaging carers in the mental health care process. They have created platforms that allow carers to voice their experiences and contribute to the care planning of their loved ones. This is part of a broader effort to embed carers’ perspectives in all levels of service delivery.
- The Trust has developed a Carers Charter, which is based on the Triangle of Care framework, ensuring that carers are recognized as equal partners in the care process. This Charter outlines the six key standards for improving the quality of care, including the involvement of carers and recognition of their expertise.
- Cultural Sensitivity and Support:
- The Trust is working to ensure that mental health services are culturally sensitive and cater to the needs of ethnic minority communities. There is a focus on improving communication between health professionals and carers, particularly in regards to understanding the cultural needs of ethnic minority patients.
- The Trust is looking to enhance its support for carers, particularly those from diverse backgrounds, by offering tailored resources and support structures. They are also aiming to create more inclusive spaces for carers to come together and share their experiences and challenges.
- Co-Production with Carers:
- Norfolk and Suffolk Foundation Trust is adopting a co-production approach, meaning that they are working collaboratively with carers and service users to design and deliver services. This approach allows carers to be actively involved in shaping policies, procedures, and the overall care framework.
- Commitment to Tackling Racial Disparities:
- The Trust is also committed to tackling racial inequalities in mental health care. They are working to ensure that ethnic minority patients and their carers have access to equitable services. This includes addressing issues such as disproportionate detention rates, increased use of restraint, and the underrepresentation of ethnic minorities in mental health research.
- Feedback and Reflection:
- Attendees were encouraged to provide feedback on the Trust’s progress, particularly on how well they felt carer voices are being integrated into mental health services. Jodie and Annie invited participants to share their thoughts and experiences to further improve services and strengthen the carer-professional relationship.
This section of the forum underscored the importance of collaborative engagement between mental health services and carers. The updates from Norfolk and Suffolk Foundation Trust highlighted how a carer-centered approach, especially one that includes the voices of ethnic minority carers, can lead to more inclusive, effective, and culturally competent care.
The next presentation was focused on Ethnic Carers and Poetry, with an emphasis on how poetry can be used as a form of expression for ethnic minority carers in mental health. The session was led by Matthew McKenzie, the facilitator of the forum.
Presentation: Ethnic Carers and Poetry
Presenter: Matthew McKenzie
In this presentation, I explored the therapeutic value of poetry in expressing the lived experiences of ethnic minority carers. I emphasized how poetry can serve as a tool to communicate the emotional burden, grief, and frustration that carers often face in mental health settings, particularly when dealing with the added complexities of racism and systemic barriers.
Key Points Covered:
- Poetry as a Voice for the Unheard:
- I discussed how ethnic minority carers, often feeling invisible within the mental health system, can use poetry to reclaim their voice and assert their lived experiences. Poetry provides a unique space for expression, where carers can share their struggles, advocate for their loved ones, and address the challenges they face in a system that may not always recognize their needs or contributions.
- Cultural Expression through Poetry:
- Poetry also allows carers to engage with their cultural heritage. For many ethnic minority carers, it serves as a means to reconnect with their traditions, cultural identity, and community. I emphasized that this form of expression can be a powerful way to resist silence and challenge marginalization within both the mental health system and society at large.
- A Call for Carers to Share Their Stories:
- I presented how important it is for carers to share their own experiences through poetry, noting that their personal stories could be transformative not just for them, but for others who face similar struggles. The opportunity to contribute their voices to the forum’s upcoming poetry collection titled “Unpaid, Unseen, Yet Unbroken” was presented as a way for carers to gain recognition and contribute to the ongoing dialogue on mental health and anti-racism.
- Poetry as Protest and Healing:
- Poetry was described as not just a form of personal expression, but also a form of protest against the invisibility and marginalization that ethnic minority carers often face in the mental health system. It was highlighted as a means to challenge institutionalized racism and raise awareness about the specific barriers faced by carers from ethnic minority backgrounds.
- Invitation for Future Submissions:
- As part of an ongoing initiative, I encouraged carers to submit their poems for inclusion in the collection. The goal was to amplify their voices, giving them an opportunity to be heard and to showcase the power of cultural expression in advocating for change.
This presentation marked an important moment in the forum, as it not only provided a space for reflection and emotional expression but also offered carers a creative outlet for advocacy and empowerment. By using poetry, carers could challenge the norms, raise awareness about the struggles they face, and ultimately drive systemic change within the mental health system.